Research
Technology for creating resilient communities
Researchers at UNC Charlotte are exploring ways to apply recent advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics to address public safety, health, transportation and other challenges facing communities. The team includes AI engineers, technology inventors, transportation experts, social and criminal scientists, and public safety experts.
The aim of this multidisciplinary team is to engage with stakeholders from the city of Charlotte, Charlotte Mecklenburg Police Department, Charlotte Department of Transportation, Central Piedmont Community College and others, including neighborhood leaders, local business owners and students to co-design a model for “Smart Cities” through the use of advanced technology.
Together they will design a sustainable, scalable model ecosystem for social good, while distinguishing Charlotte, North Carolina, as a “Community-Based Technology Inventor for the Future.”
Technology-Driven Outcomes
The team will develop novel transformative cloud-to-edge AI processing systems that create:
- Extensible, community-driven data collection and processing designed to alleviate concerns related to data privacy and security.
- A self-aware network of smart Internet-of-things (IoT) devices, including cameras and sensors that possess on-the-fly AI-processing capabilities.
- A proactive mechanism that ensures privacy while identifying macro/micro scalable behaviors, transactions, and demand/supply chains without detecting or storing information related to identities of citizens.
Targeted areas include public safety, smart transportation, circular economy and a broader range of applications that require real-time situational awareness and decision making.
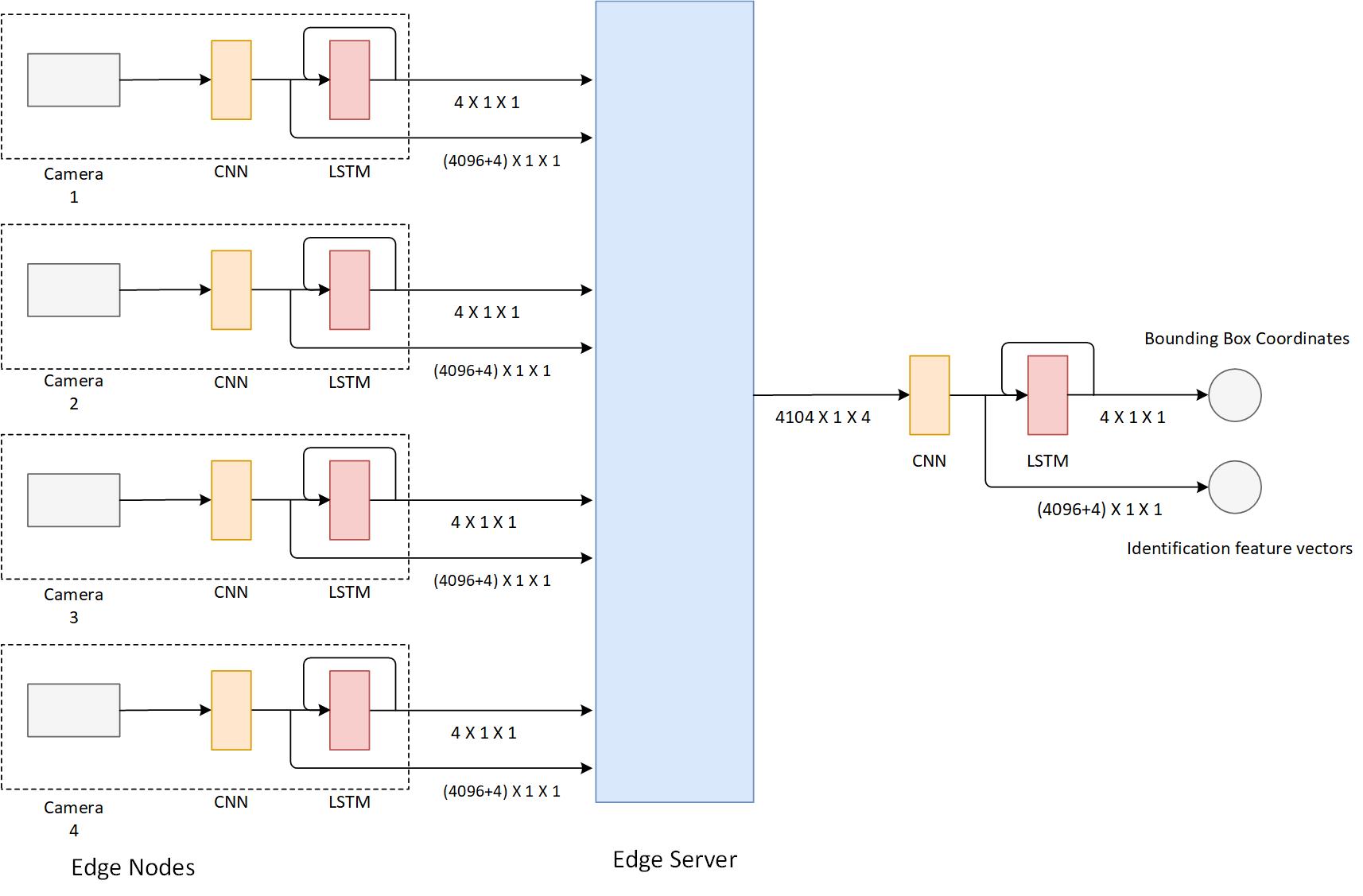
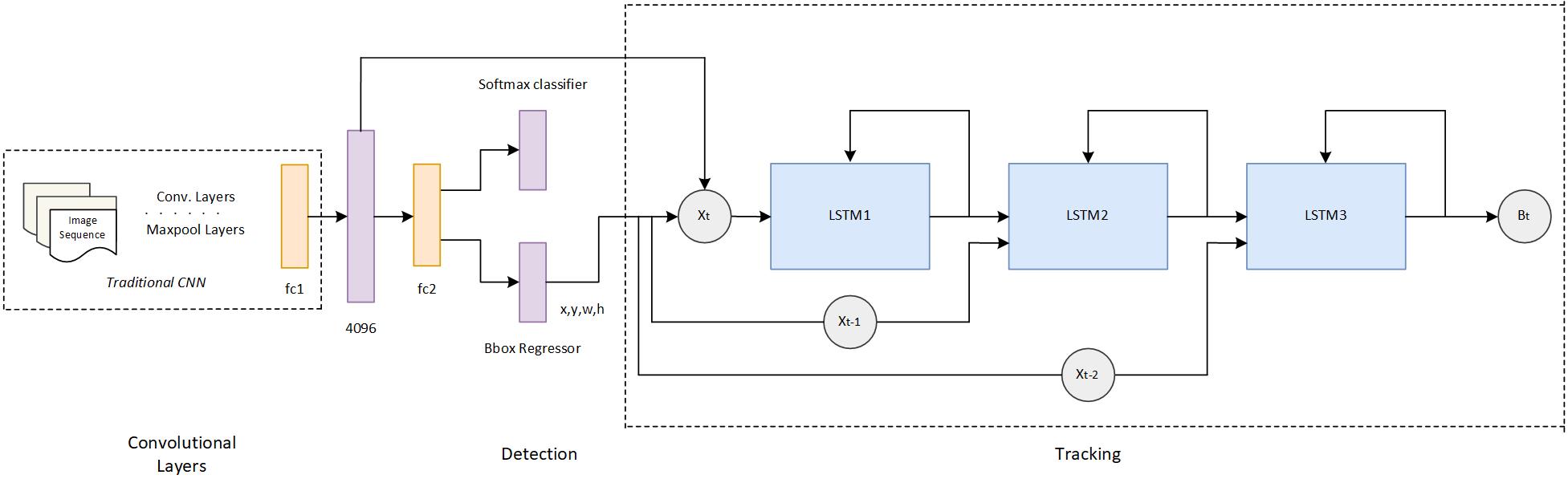
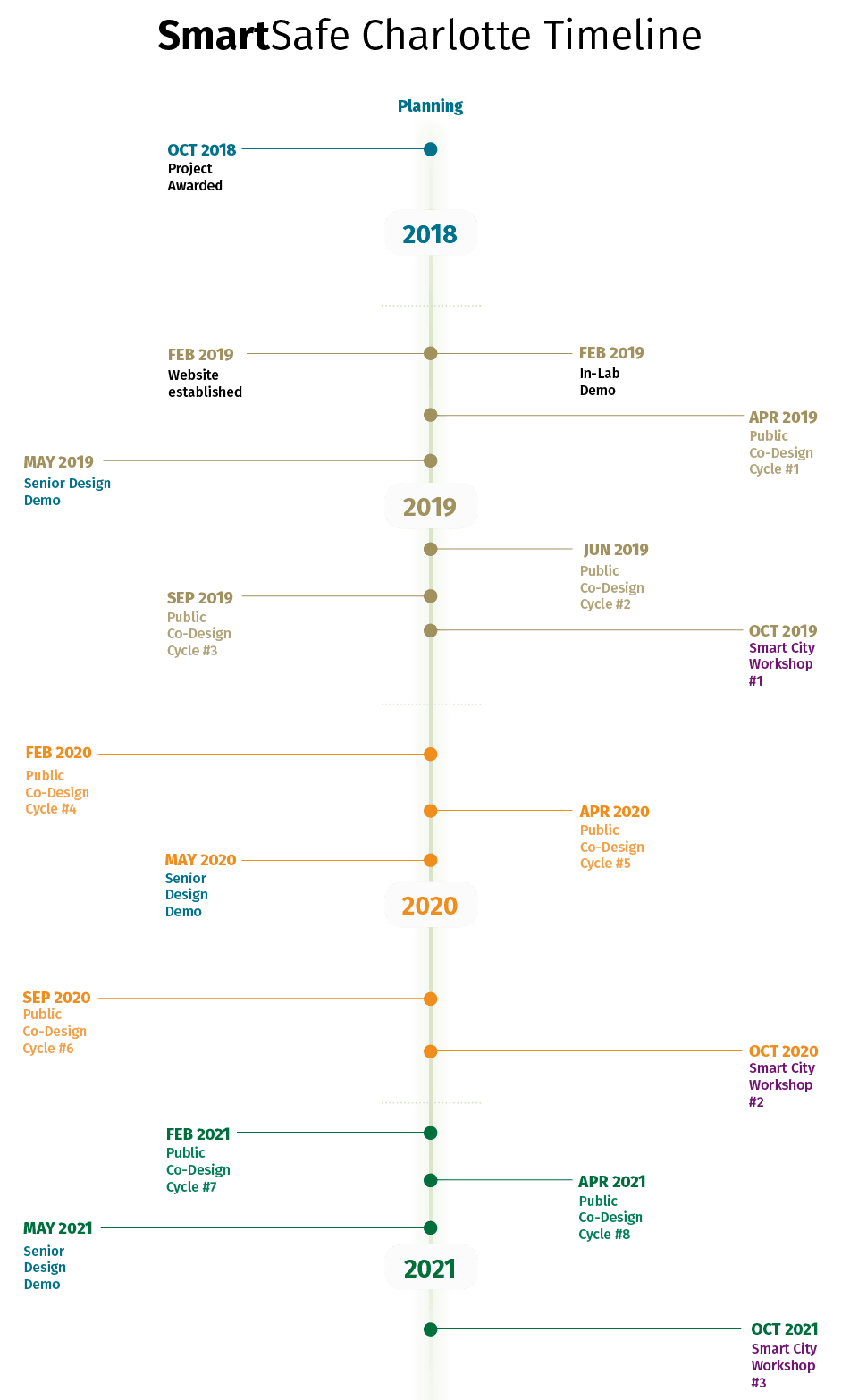
The team has received multiple local and federal grants including the recently announced major NSF Smart and Connected Communities award, ”SCC: Building Safe and Secure Communities through Real-Time Edge Video Analytics” – (2018-2022) NSF Award No. 1737586, IRB Approved Study #18-0452.